Anaerobic Glycolysis Can Supply Energy to Muscle Tissue for
Therefore for glycolysis to play a key role in energy metabolism by producing adenosine triphosphate ATP while simultaneously providing the main aerobic substrate pyruvate for the TCA cycle assigning such a role to lactate was inconceivable. All Anaerobic glycolysis can supply energy to muscle tissue for 10 to 30 seconds.

Anaerobic Glycolysis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
The disadvantage of anaerobic glycolysis in high-intensity muscle contractions is that.
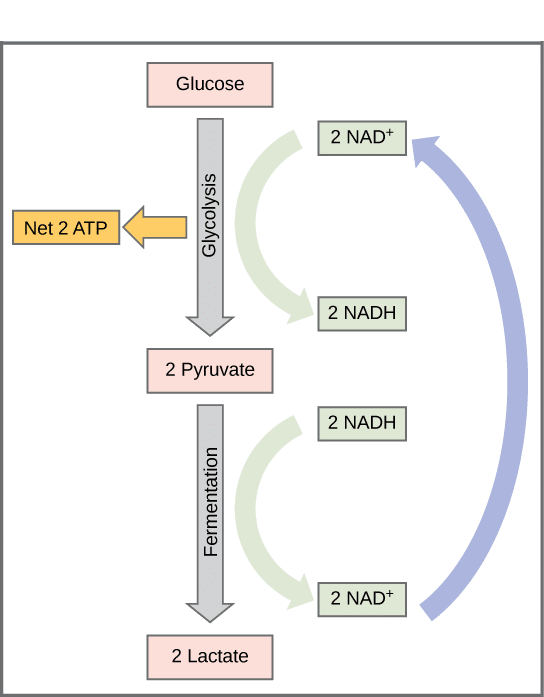
. 1 It is inefficient from an energetic standpoint and produces only two ATP molecules per glucose molecule which is 19 times less than the full energy potential of a glucose molecule. Anaerobic glycolysis can supply energy to muscle tissue for 30 seconds - 2 minutes The disadvantage of anaerobic glycolysis in high intensity muscle contractions is that ATP production cannot be sustained for long events The site of greatest energy production in. This process takes place in the cytoplasm and despite the rapid ATP synthesis anaerobic glycolysis is less efficient than aerobic glycolysis.
Broken down there are about 100g of glycogen in the liver and upwards of 400g of stored glycogen in muscle tissue. -Phosphagen system a few seconds -Anaerobic fermentation less than 2 minutes. In rapidly contracting skeletal muscle cells with energy demand exceeding what can be produced by oxidative phosphorylation alone anaerobic glycolysis allows for the more rapid production of ATP3 Glycolysis is approximately 100 times faster than oxidative phosphorylation.
2 to 5 minutesD. This process releases energy very rapidly and will produce enough energy to last about 90 seconds. How long can anaerobic glycolysis supply energy to muscle tissue.
Glycolysis is also called short term energy system and lactic acid system. It is used during high-intensity sustained isometric muscle activity. 10 to 30 secondsB.
It is important that oxygen is not required because it takes the heart and lungs some time to get increased oxygen supply to the muscles. In glycolysis a single glucose molecule is broken down within the cytoplasm of a cell into two molecules of pyruvate. Anaerobic glycolysis can supply energy to muscle tissue forA.
30 seconds to 2 minutesC. ATP production cannot be sustained for long events The disadvantage of anaerobic glycolysis in high-intensity muscle contractions is that. Glycogen is stored in muscle tissue and the liver and the average person holds about 1500-2000 calories of stored glycogen.
Muscle fatigue which has many contributing factors occurs when muscle can no longer contract. 30 seconds to 2 minutes Anaerobic glycolysis can supply energy to muscle tissue for how long. An oxygen debt is created as a result of muscle use.
3 Glycolysis is approximately 100 times faster than oxidative phosphorylation. In rapidly contracting skeletal muscle cells with energy demand exceeding what can be produced by oxidative phosphorylation alone anaerobic glycolysis allows for the more rapid production of ATP. Up to 30 minutes.
Loose Leaf Version for Perspectives in Nutrition 9th Edition Edit edition Solutions for Chapter 11 Problem 15MCQ. Anaerobic glycolysis produces small amounts of ATP in the absence of oxygen for a short period. Skeletal muscle fibers can get ATP from 3 sources.
30 seconds to 2 minutes. Anaerobic glycolysis is the main metabolic pathway used in the setting of limited oxygen supply during exercise. This glycolysis respiration can produce energy quickly only 2 ATP for intensive demands but less efficiently than mitochondrial respiration total 36-38 ATP.
When the oxygen supply runs short in heavy or prelonged excercise muscles obtain most of their energy from an anaerobic without oxygen process called glycolysis. In an ischemic state such as during a heart attack or even during the induced ischemia of open heart surgery there is. Anaerobic metabolism in heart muscle plays a role in maintenance of myocardial preservation only during ischemia or hypoxia.
Stimulation of the motor nerve to the muscle in vivo depleted the high-energy phosphates to a greater extent and elicited a higher rate of anaerobic glycolysis in the white fibres than in the red. Mitochondria The site of the greatest energy production in a muscle cell is the what. Anaerobic glycolysis is involved in muscular activities that last for as short a period as a few minutes with high energy demand where aerobic metabolism is not adequate for the energy requirements.
Muscles generate force needed for all our daily activities including walking standing running and lifting weights. The main provider of ATP during intense exercise that lasts 10 120 seconds. Glycolysis alone can provide energy to the muscle for approximately 30 seconds although this interval can be increased with muscle conditioning.
On the contrary they are rich in glycogen and enzymes of glycolysis. Muscle Contraction Energy Muscles use ATP to contract which is produced by aerobic and anaerobic glycolysis in muscle tissues. This system uses glucose in the.
The breakdown of carbohydrates to provide energy without oxygen is called anaerobic glycolysis. Skeletal muscle fibers can get ATP from 3 sources. Aerobic metabolism utilizes oxygen to produce much more ATP allowing a muscle to work for longer periods.
Anaerobic glycolysis Anaerobic glycolysis is the main source of energy production in situations where oxygen demand exceeds oxygen supply such as an intense exercise. -Phosphagen system a few seconds -Anaerobic fermentation less than 2 minutes. All of the choices are correct.
Therefore they are very effective for powerful and rapid contraction of short duration fueled by anaerobic metabolism. 2 to 5 minutes. As an exercise continues more than 10 seconds the anaerobic glycolytic system takes charge of providing ATP.
How long can anaerobic glycolysis supply energy to muscle tissue. 30 seconds to 2 minutes. Up to 30 minutes.
White muscle fibers contain less myoglobin and mitochondria and have a poor blood supply compared to red muscle fibers. Estimated4 minsto complete Progress Practice Muscle Contraction Energy Practice Add to Library Details Resources Download Quick Tips NotesHighlights Vocabulary Muscle Contraction Energy Supply - Advanced Loading. The results indicated that white fibres depend more than red on anaerobic mechanisms for their supply of energy.
While the pyruvate generated through glycolysis can accumulate to form lactic acid it can also be used to generate further molecules of ATP. The energy for glycolysis comes from glucose or our stored form of glucose glycogen. Muscles produce lactates by anaerobic glycolysis.

Muscle Energy Systems Mobility Health

No comments for "Anaerobic Glycolysis Can Supply Energy to Muscle Tissue for"
Post a Comment